An automation engineer specializing in SCADA systems designs and configures solutions to monitor, control, and optimize complex energy infrastructures—from substations to entire plants such as photovoltaic parks and battery energy storage systems (BESS).
SCADA System Components:
• Intelligent Automation: Programming logic for devices like PLCs and RTUs to ensure smooth and autonomous system operation. Some examples include:
- ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch): Managing the automatic transition between power sources to ensure uninterrupted service.
- SHG (Self-Healing Grid): Configuring networks capable of detecting and isolating faults, restoring power automatically without operator intervention.
• Protection Relays: Implementing systems to detect anomalies and protect critical equipment.
📟 RTUs and the Intelligence of Ring Networks:
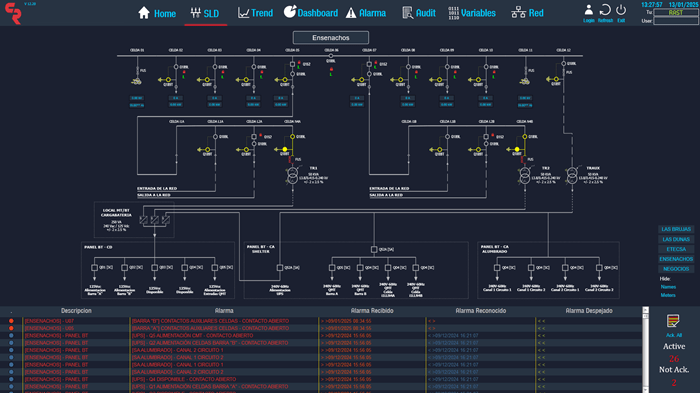
“One of the most interesting projects I’ve worked on,” says Stefano Barbera, automation technician, “was the automation of ring network substations in medium voltage systems.” Here’s how Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) have transformed these infrastructures:
• Continuous Monitoring: RTUs are configured to collect real-time data (voltage, current, power) and transmit it to the SCADA system, ensuring constant network supervision.
• Advanced Diagnostics: RTUs detect and locate faults, enabling quick and targeted interventions.
• Automatic Switching: Logic programming for fault isolation and power restoration to healthy sections, improving network reliability.
• Operational Optimization: Implementing algorithms to reduce losses and enhance overall system efficiency.
Thanks to these solutions, ring networks become smarter and more resilient, reducing downtime and improving service quality for end users.
💻 Technical & IT Perspective:
• Server-Client Programming: Designing and configuring server-client architectures for SCADA systems, ensuring seamless communication between components.
• Network Redundancy: Implementing redundant networks to guarantee reliability and continuity, even in case of hardware failures or communication interruptions.
• SCADA Panels: Managing switches and firewalls to maintain security and system stability.
• Protocols & Communication: Utilizing standards such as IEC 60870-5-104, IEC 61850, and Modbus, and technologies like Ethernet, fiber optics, and 4G to create a robust and high-performance network infrastructure.
By integrating SHG logic, protection relays, and redundancy systems, downtime is minimized, and operational continuity is ensured. At the same time, automated management helps reduce energy waste, improving efficiency and sustainability. From small plants to large substations, every infrastructure is designed to be reliable and monitored in real-time.
“Every day brings new challenges, but knowing that I contribute to a safer and more sustainable energy future makes every effort truly rewarding!” With this enthusiasm, Stefano configures SCADA interfaces for our clients and conducts training sessions for software usage.